

In Excel, never do math in your head and type the answer in a cell where you would expect to have a formula calculate the answer.īefore moving on, let's explore some more formulas to make sure you understand the order of operations by which Excel calculates an answer. When using formulas with cell references, the results change each time the numbers are edited.

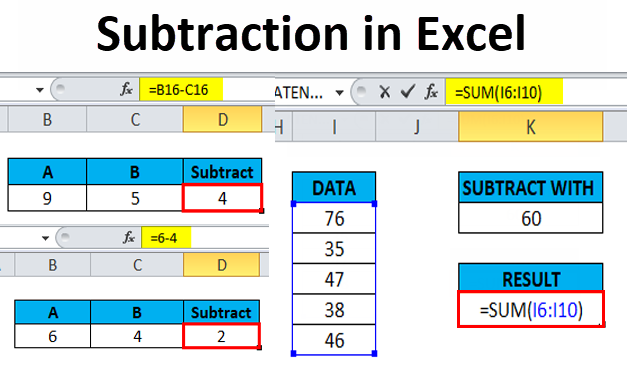
Calculate the operation in parenthesis (6-4), where the answer is 2.You must follow the order of operations to get the correct answer. Is the answer 8 or 4? If you ignored the parentheses and calculated in the order in which the numbers appear, 2*6-4, you'd get the wrong answer, 8. Using this order, let us see how the formula 120/(8-5)*4-2 is calculated in the following picture: Addition and subtraction, whichever comes first.Multiplication and division, whichever comes first.Exponential calculations (to the power of).If you enter a formula that contains several operations-like adding, subtracting, and dividing-Excel XP knows to work these operations in a specific order. The order of mathematical operations is important. Complex formulas involve more than one mathematical operation. You may also try =65941.008- 65941.0016 with 18 or more decimal places displayed.Simple formulas have one mathematical operation. The effect may manifest itself as a stepping forward of insignificant digits.Ĭoncerning your example this was the final effect. See this paragraph in the English wikipedia and the article it is contained in. 2- Cancellation of significant digits by subtraction. Exact conversion from dyadic to decimal is only generally possible (in an impractical sense) if as many decimal digits are allowed as dyadic digits were used (which are in practice 52 for most computer applications). Exact conversion from decimal to dyadic is strictly impossible for most non-integer starting values.
1- There is no way to get generally closed round-trips by conversion between the dyadic and the decimal representation of numbers with fixed lengths (numbers of digits) for either system. There are two effects concerning non-integer arithmetic involved: The answer below uses the more correct term “dyadic representation”.) (The answer expects everybody to know that “computers calculate with binary numbers”.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
